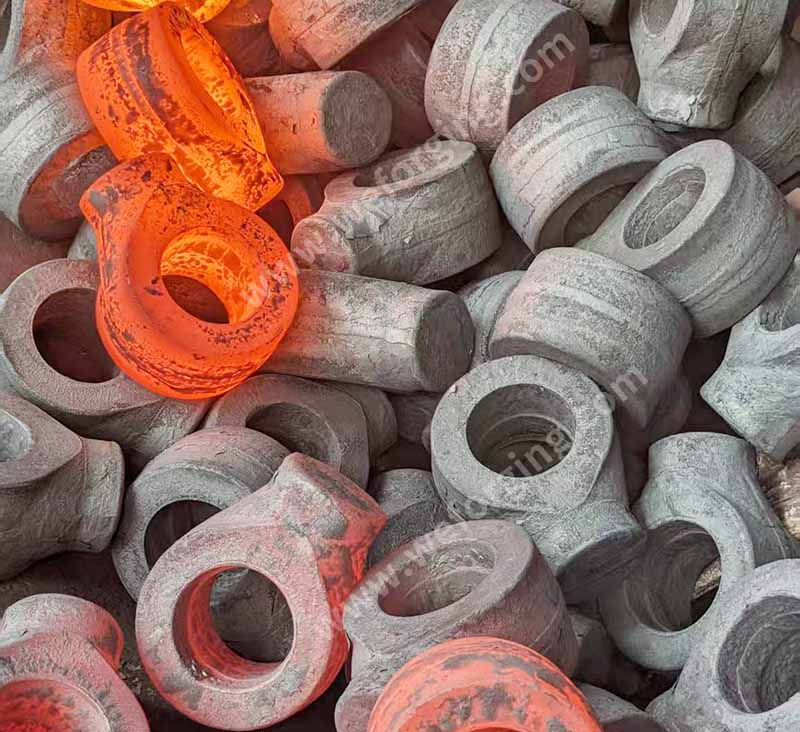
What are the benefits of forgings?
Why do industries such as automobiles,
aerospace, ships, mechanical equipment and heavy engineering vehicles need a large number of forgings? Compared with other metal forming processes, what advantages does hot die forging have? This article will explore the main advantages of forgings and why they are the preferred choice in high-performance applications.
1.Higher mechanical performance
✔ Strength and toughness:
Forging refines grains through physical deformation and eliminates internal defects (such as pores and shrinkage porosity) at a certain forging ratio, making the flow of metal fibers more continuous. This significantly enhances tensile strength, fatigue strength, and impact toughness. Therefore, the fatigue life and toughness of forgings are several times higher than those of castings.
✔ Good metal flow:
Forging can directionally arrange grains (such as the streamline distribution in die forging), making mechanical properties better in a specific direction. In contrast, the anisotropic properties of castings are usually uniform but weak, and they are prone to have weak points.

2. Better organizational performance
⊗ After heat treatment, the yield strength can be enhanced, resulting in higher impact resistance
The microstructure is good after heating, so the mechanical properties are uniform and stable
✔ Compactness: The forged parts have almost no casting defects such as pores and shrinkage cavities, and the internal structure is highly dense. They have a stronger load-bearing capacity and are safer under high pressure and high load conditions.
✔ Low defect rate: Casting is prone to problems such as slag inclusion and sand holes, has poor density, and is highly related to the humidity of the weather.
3. Material utilization rate and cost balance
Less material waste (near net molding)
✔ Fewer machined dimensions
The stress deformation is smaller because the quality is dense and uniform. The core of pure machined bar stock will be slightly thinner
✔ Superior to pure machining: If certain parts of the workpiece do not need to be machined or arc-shaped, forging near-net forming can reduce the amount of subsequent processing and save materials (precious alloy materials), while pure machining will waste a large amount of raw materials.
✔ Superior to casting: Although casting offers higher shape freedom, forgings can achieve their goals through a small amount of subsequent processing in medium-complexity parts, and they perform better.
4. Special environmental adaptability
✔ High/low temperature performance: The uniform structure of the forged part has a stronger resistance to creep and brittle fracture at extreme temperatures. For example, the turbine disk must be forged to withstand high-temperature stress.
✔ Corrosion resistance: The dense structure reduces the penetration of corrosive media, and it is easier to create an anti-corrosion depth on the steel surface during surface treatment. Therefore, it is more corrosion-resistant than porous castings.
5. Lightweighting potential
♦Under the same strength, forgings can be designed to be thinner and lighter (such as articulated arms), while castings need to increase the wall thickness to compensate for the strength disadvantage.
Comparison and Summary Table
Characteristics:
♦Forged parts, cast parts, and pure machined parts
The mechanical strength is the highest (grain refinement), the lower (possible defects exist), and the core is sparse
The toughness is excellent (the fiber flow direction is controllable), but generally (the grains are coarse) and uneven
The defect rate is extremely low and relatively high (porosity, shrinkage porosity), with a certain degree of stress release
Material utilization rate: medium-high (near net forming), high (complex shapes), low (large cutting waste)
The cost is medium (high mold cost), low (for large quantities), and high (material + labor cost).
Applicable scenarios: high load, key components, complex gear shapes, and small batches of low-stress components
6. Mass production is more cost-effective
Although the initial mold cost is relatively high, forging is economically significant and efficient in large-scale production because:
Less material waste (near net molding)
Greatly reduce machining time
The service life of molds is longer than that of casting
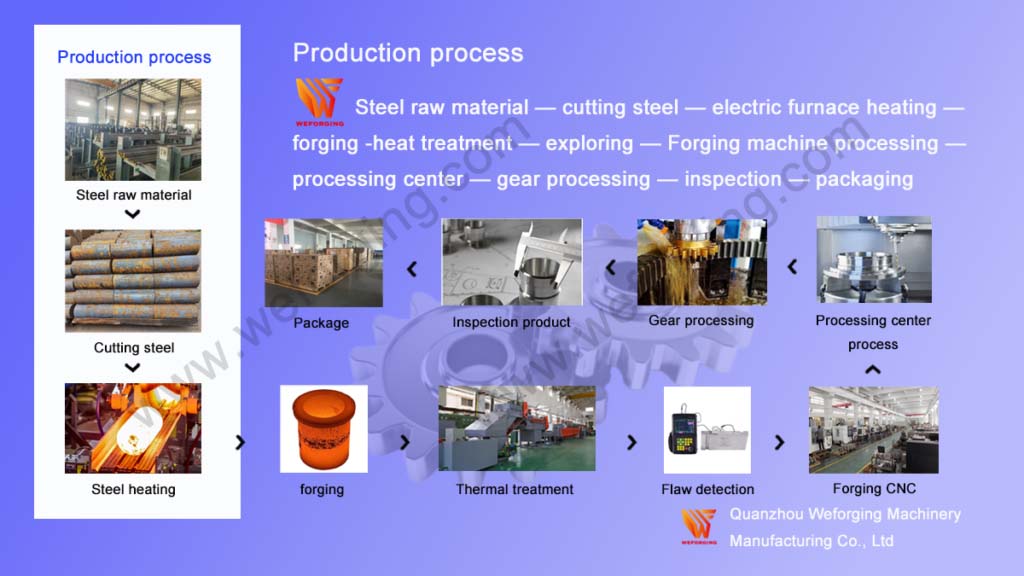
Reliable guarantee of hot forging/cold forging in critical applications
Forgings are indispensable in the field of zero potential safety faults:
Gearbox and transmission System (high-load scenarios)
✔ Energy/Agricultural machinery industry (Corrosion-resistant forgings)
Heavy equipment hydraulics (Cylinders for mining and construction machinery)
Reasons to choose Weforging:
✅ More than 40 years of forging experience
✅ Forging laboratory, flaw detection equipment
✅ ISO 9001 & AS9100 certification
✅ Global supply chain guarantees fast delivery
Your forging solution provider:
Forging manufacturers offer unparalleled strength, durability and cost-effectiveness for demanding industrial applications. Whether you need custom-made forgings or machined parts in bulk, Weforging can provide you with high-quality solutions. We will tailor the product process according to your application scenario and strictly follow the technical requirements.
Contact us immediately to discuss your project requirements!
📧 Email: [email protected]