Cold Forging Services for Precision Industrial Components
Cold forging—also known as cold forming—is a metal-forming process performed at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures. By applying high pressure through precision tooling, metal flows into the desired shape without melting or extensive heating. This method produces strong, accurate, and repeatable components that are ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
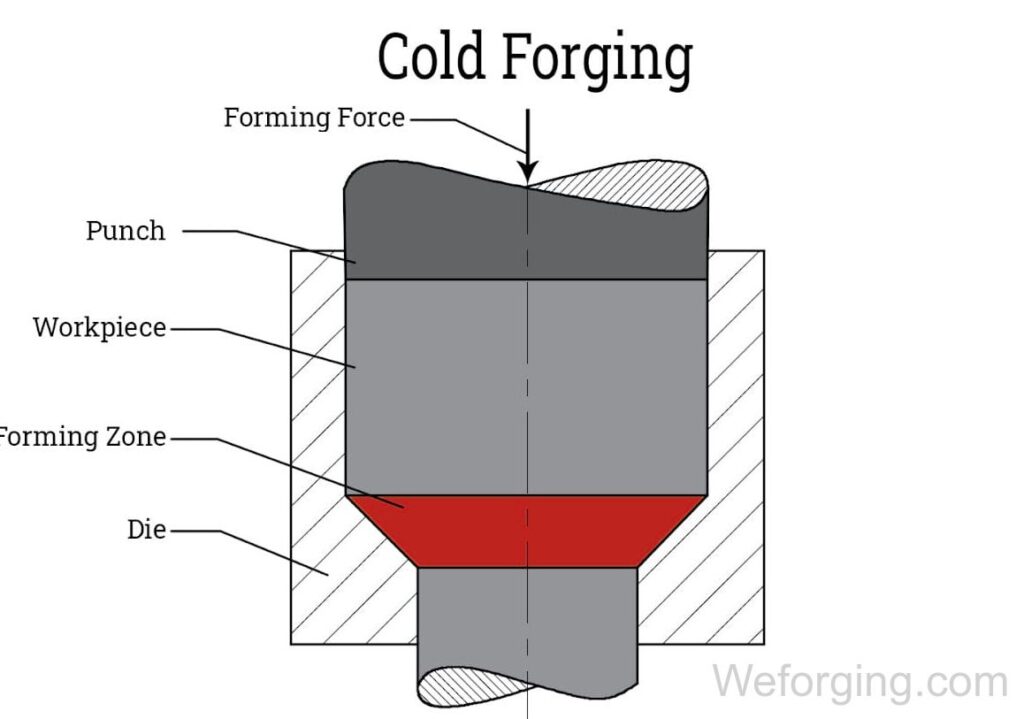
How the Cold Forging Process Works
The cold forging process typically includes several forming operations, such as cold heading, cold extrusion, closed-die forming, and multi-station progressive forging. During deformation, grain flow follows the shape of the part, improving strength and fatigue resistance. Cold forging presses, high-strength dies, and proper lubrication are essential to achieving consistent performance and tight tolerances.
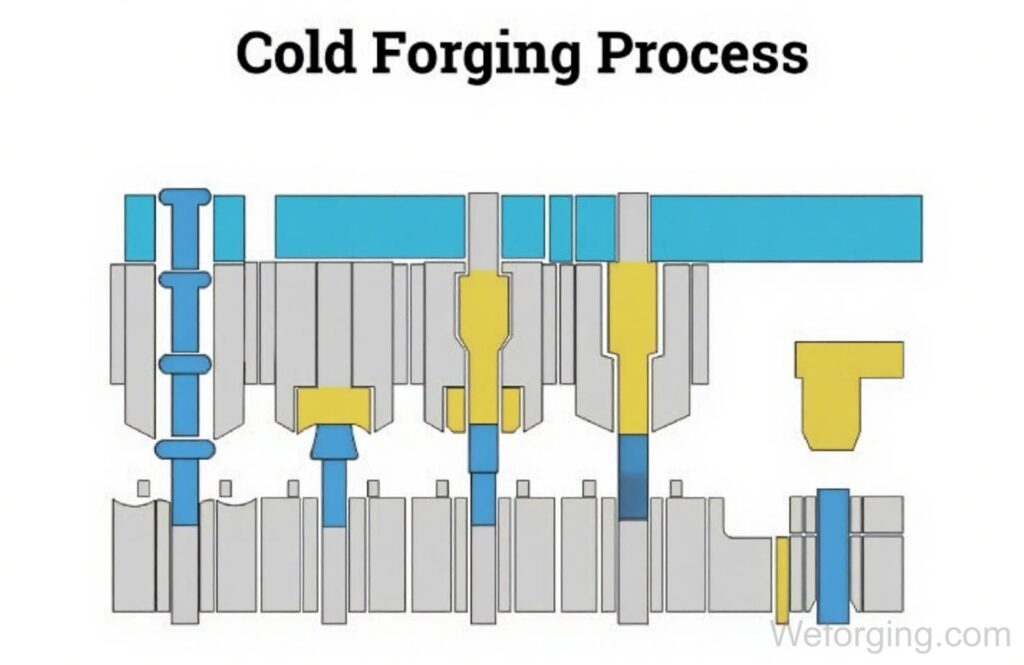
Types of Cold Forging Processes
Cold forging is not a single forming method. Different cold forging processes are selected based on part geometry, deformation ratio, and production volume. At Weforging, multiple cold forging techniques are applied to achieve stable forming quality and consistent dimensional accuracy.
Cold Heading
Widely used for fasteners and connectors such as bolts, nuts, and studs. This process offers high productivity and excellent material utilization for mass production.Cold Extrusion
Suitable for sleeves, bushings, and hollow components. Cold extrusion improves fiber flow continuity and enhances mechanical strength without additional heating.Multi-Station Cold Forging
Applied to complex parts requiring multiple forming steps. Progressive forming improves dimensional consistency and repeatability in high-volume production.Closed-Die Cold Forging
Used for precision components with defined geometries. This method supports near-net shape forming with minimal secondary machining.
Cold-Forged Products
Cold-Forged Fasteners & Connectors
Bolts, nuts, double-ended studs, sleeves, and bushings widely used in automotive and industrial systems.
For larger or more complex shapes, we also offer hot forging solutions to handle components that require high deformability.
Small Shafts & Transmission Blanks
Cold-forged small shafts, stepped shafts, splined sleeves, and gear or sprocket blanks suitable for precision machining.
Parts requiring tighter tolerances can be finished through our CNC machining services for final accuracy.
Mechanical ConnectorCNC-Bearbeitung Parts
Compact couplings, rod-end blanks, and structural connectors that benefit from stable cold-forming performance.
When gear-related profiles or splines are required, they can be completed using our gear machining capabilities.
Cold-Forged Components for Machinery Systems
Small housings, plugs, and precision blanks designed for further CNC finishing or heat treatment.
These components integrate seamlessly with our machining and hot forging workflow, offering a complete forging-to-finish manufacturing solution.

Cold Forging Capability Range
Cold forging is most effective when applied within defined dimensional and production limits. Typical cold forging capability ranges include:
Part size: small to medium-sized components
Dimensional accuracy: tight tolerances suitable for precision assembly
Surface finish: smooth surfaces with minimal post-processing
Production volume: medium to high-volume production programs
Secondary operations: CNC machining and heat treatment available when required
This capability range allows cold forging to deliver cost efficiency, dimensional stability, and consistent quality in mass production.
Advantages of Cold Forging
Cold forging offers several engineering and commercial advantages:
Excellent mechanical strength due to refined grain flow
High dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish
Near-net-shape capability with minimal machining
High material utilization, reducing production waste
Lower energy consumption compared with hot forging
Cost-effective for small to medium-sized parts in large quantities
These benefits make it a preferred method for producing precise and durable components.
Cold Forging vs. Hot Forging
| Category | Cold Forging | Hot Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Performed at room temperature with no heating required | Metal is heated to 900–1200°C before forming |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Excellent accuracy; minimal deformation | Lower accuracy due to thermal expansion |
| Strength Performance | Higher strength from grain flow and work hardening | Good strength but often requires heat treatment |
| Forming Complexity | Best for small to medium parts with simpler shapes | Suitable for large, complex, or hard-to-form shapes |
| Surface Finish | Smooth surface; minimal secondary machining | Rougher surface; machining is usually required |
| Energy Consumption | Low energy usage | High energy consumption due to heating |
Materials for Cold Forging
Common cold forging materials include carbon steels (C10–C45), alloy steels such as 20Cr, 40Cr, and 42CrMo, stainless steels (304, 316, 410), aluminum alloys, copper, and brass. These materials offer good plasticity at room temperature and maintain stable flow during deformation. Selection depends on forming difficulty, required mechanical strength, surface finish expectations, and the final application environment, ensuring both manufacturing efficiency and long-term component reliability.
Applications of Cold Forging
Cold forging is widely used in applications where dimensional accuracy, material strength, and production efficiency are critical. The process is particularly suitable for high-volume manufacturing of small to medium-sized components.
Typical cold forging applications include:
Fasteners and Connectors
Bolts, nuts, studs, bushings, and sleeves requiring high strength, tight tolerances, and consistent batch quality.Automotive and Transportation Components
Precision cold-forged parts used in engines, transmissions, and chassis systems, where fatigue resistance and reliability are essential.Power Transmission and Mechanical Systems
Shafts, splined components, and gear blanks that benefit from refined grain flow and stable dimensional accuracy.Industrial Machinery and Equipment
Structural connectors and functional components designed for long service life and repeatable performance in industrial environments.Components for CNC Finishing Operations
Cold-forged blanks supplied for subsequent CNC machining when tighter tolerances or complex features are required.
These applications benefit from cold forging’s ability to deliver near-net shape components, reduced material waste, and stable quality in mass production.
Why Choose Weforging for Cold Forging
Weforging provides integrated cold forging solutions for OEM and industrial applications requiring precision, strength, and production stability.
Key advantages include:
Cold forging combined with CNC machining
Forged parts can be supplied near-net shape or finished through CNC machining for tighter tolerances.In-house tooling and process design
Forming processes are engineered to support stable deformation and consistent quality.High-volume production stability
Cold forging processes are optimized for repeatability and long-term batch consistency.Material and standards alignment
Carbon steels, alloy steels, and stainless steels aligned with international standards.OEM and export project experience
Support for global OEM programs with defined documentation and quality control.
Contact
If you are sourcing cold-forged parts or need engineering support for a new project, our technical team is ready to assist with design evaluation, material recommendations, and full-process manufacturing.
Contact us to request a quotation or discuss your application requirements — we respond quickly and provide professional guidance for global OEM and industrial customers.

