Which is Better: Cold or Hot Forging?
In modern manufacturing, forging is one of the most reliable methods to produce strong, precise metal parts. But when choosing between cold forging and hot forging, many buyers wonder: what’s the real difference? Understanding this helps you select the right process for custom forged components, ensuring you get the best performance, cost, and quality.
In this article,Weforging Manufacturing will explain the key differences, applications, advantages, and typical industries using each process.
Hot Forging vs Cold Forging: Which Should You Choose?
When comparing hot forging vs cold forging, the best choice depends on part size, material strength, and required precision.
Cold forging is typically preferred for high-volume production of small parts that require tight tolerances and good surface finish, such as fasteners and precision components.
Hot forging, on the other hand, is more suitable for large or high-strength components, including shafts, gears, rings, and heavy-duty parts where superior mechanical properties are required.
In industrial manufacturing, cold forging focuses on precision and efficiency, while hot forging supports strength and complex heavy components.
What is Cold Forging?
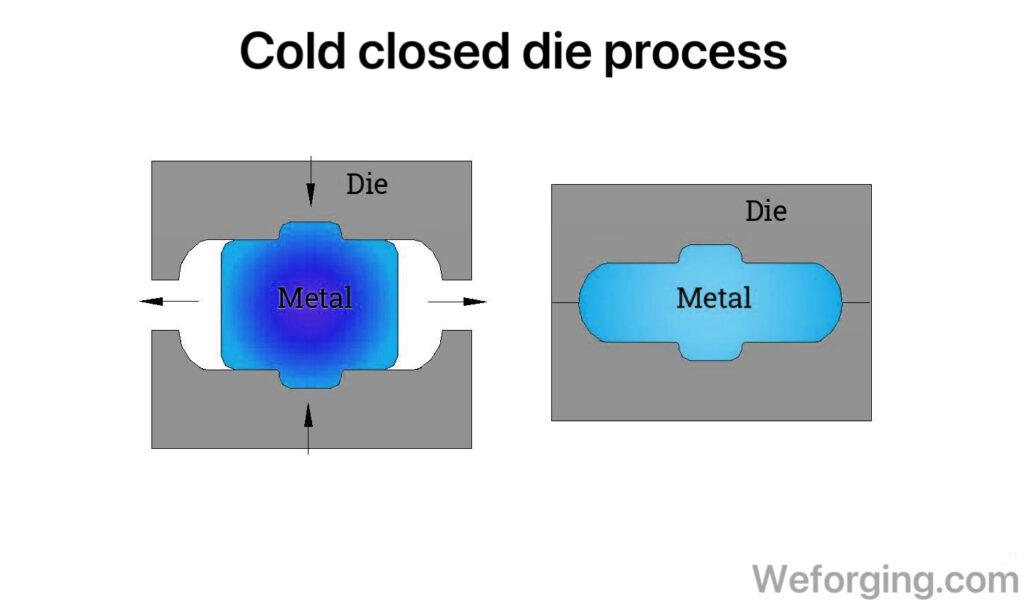
Cold forging, also known as cold forming, is a forging process done at or near room temperature. The metal is forced into a die under high pressure.
Cold forging is ideal for creating precision forged parts with excellent surface finish and tight tolerances.
Main Features of Cold Forging
No heating required
→ Results in significantly lower energy costs.High dimensional accuracy
Forging precision can be controlled to about ±0.1 mm per side.
For unprocessed surfaces, this reduces subsequent machining costs.
Smooth surface finish
Free of oxide scale, improving surface quality and reducing secondary processing needs.
Material limitations
Suitable for relatively soft metals, such as 1045, 20#, and materials with low alloy content.
Smaller components
Cold extrusion capacity
Allows slightly larger parts (typically up to 1–2 kilograms), depending on material and shape:
splined shafts, sleeves, and retaining rings.
Batch quantity requirement
Due to the high cost of molds, cold forging is suitable for mass production only.
For example, cold-forged fasteners typically require 200,000+ pcs per batch to be cost-effective.
What is hot forging?
Hot forging refers to the deformation of metals above their recrystallization temperature, typically between 900°C and 1250°C for steel.
Heated metals are malleable, thus making it easier to shape large and complex components.
Hot Forging: Key Features & Applications
Material Compatibility
Applicable to various metal materials and high-strength alloys
Forming Capabilities
Superior formability for large parts
Reduces internal stress
Improves grain structure
Process Characteristics
Requires larger product allowances due to high forging impact force
May need additional processing for precision improvement
Higher material consumption but greater versatility
Surface Considerations
Oxide scale formation on surface
Requires secondary treatments (e.g., shot blasting)
Typical Products
Flanges
Heavy custom forgings for:
✓ Automotive industry
✓ Heavy machinery
Cold Forging vs. Hot Forging: Key Differences
Feature | Cold Forging | Hot Forging |
Temperature | Room temperature | 900–1250°C |
Material Hardness | Softer metals preferred | Works with tough alloys |
Accuracy | High precision | Good, may need machining |
Energy Use | Lower | Higher (heating required) |
Typical Parts | Fasteners, small precision components | Gears, ring forgings, shafts, heavy-duty parts |
Different industries select cold or hot forging based on performance and production requirements:
Cold Forging Applications
Automotive fasteners and connectors
Bolts, nuts, and precision metal fittings
Small shafts and sleeves
High-volume precision components
Hot Forging Applications
Gear blanks and transmission parts
Large shafts and flanges
Ring forgings and heavy machinery components
Structural parts exposed to high loads
Cold forging is ideal where dimensional accuracy and production efficiency are critical, while hot forging is chosen when strength and load capacity are priorities.
Choose cold forging when:
Producing high-volume small parts
Tight tolerances and good surface finish are required
Parts such as fasteners and precision components are needed
Choose hot forging when:
Manufacturing large or high-strength components
Parts must withstand heavy loads or impacts
Products include gears, shafts, or ring forgings
In summary: Cold forging is ideal when precision and production efficiency are priorities, while hot forging is preferred for larger components requiring higher strength and durability in demanding industrial applications.
Benefits of Weforging Manufacturing’s Custom Forging
At Weforging Manufacturing, our custom forging services combine cold and hot forging processes to support diverse industrial applications.
We control the full production process — from material selection and forging to CNC machining, heat treatment, and final inspection — ensuring stable quality and reliable results across batches.
Our integrated facilities efficiently produce precision fasteners, ring forgings, and complex gear components, helping customers achieve consistent quality, shorter lead times, and dependable long-term performance.
Watch How We Forge
Below is a short video from our Weforging YouTube channel showing a quick look at our forging lines:
Conclusion
Choosing between cold forging and hot forging depends on your product requirements — size, material, precision, and budget.
Partnering with an experienced supplier like Weforging Manufacturing helps you get high-quality, cost-effective forged parts that meet your exact specifications.
If you’d like to discuss your custom forging project, feel free to contact us today!

