Why is Forged Steel Stronger?
In modern industrial manufacturing, forged steel is widely used in applications where strength, durability, and reliability are critical. However, not all steel components perform the same. Engineers and procurement teams often ask: Why is forged steel stronger than cast or machined steel?
The answer lies in how the metal is formed and how its internal structure responds to load. This article explains why forged steel is stronger by examining the forging process, grain flow behavior, defect reduction, mechanical properties, and typical industrial applications.

Why Is Forged Steel Stronger Than Cast Steel?
Forged steel is stronger than cast steel because the forging process reshapes solid metal through compressive force, creating continuous and directional grain flow. This refined grain structure follows the load path of the component, significantly improving strength, fatigue resistance, and impact toughness.
Cast steel, by contrast, is formed by pouring molten metal into molds. During solidification, internal porosity and non-uniform grain structure may occur, which can reduce mechanical reliability under cyclic or high-stress conditions. For load-bearing and safety-critical components, forged steel is therefore generally preferred.
What is Steel Forging?
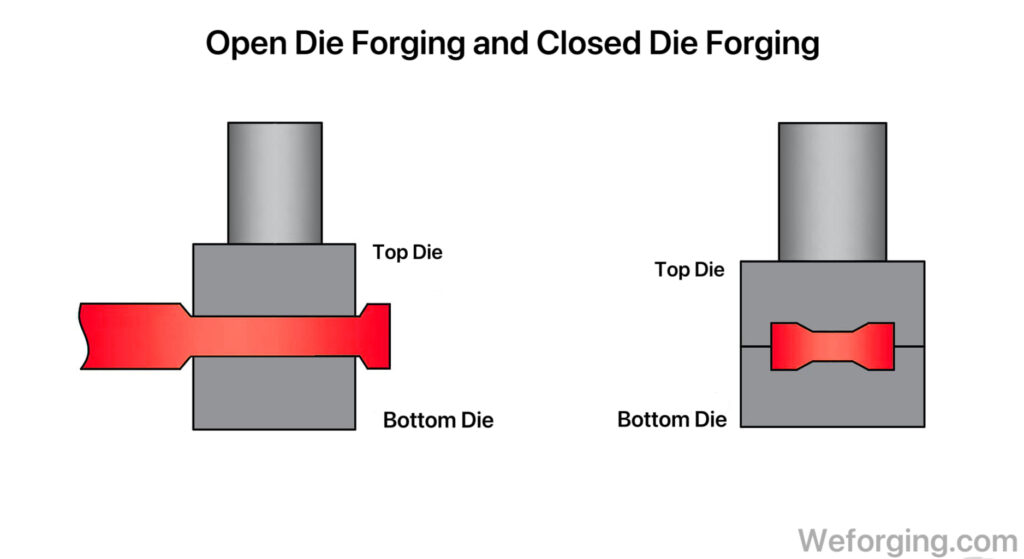
Steel forging is a manufacturing process that uses localized compressive forces to shape metal. Unlike casting, where molten steel is poured into a mold, forging applies mechanical force to transform solid steel into the desired shape. Common methods include open-die forging, closed-die forging, and ring forging. This process aligns the steel’s internal grain structure, which is the key to its superior strength.The forging ratio of this process significantly enhances the material’s density and reduces porosity and other phenomena, which is unmatched by other processes.
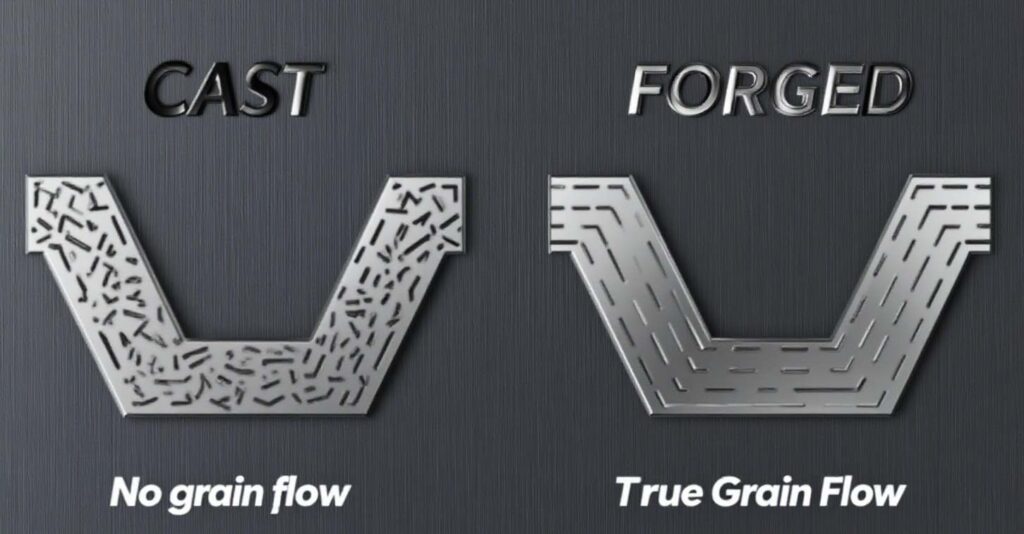
Grain Flow: The Secret to Strength
One major advantage of forged components is the improved grain flow. When steel is forged, its grains follow the shape of the part rather than being random as in castings. This directional grain structure greatly increases tensile strength and resistance to impact. For example, a forged gear can handle higher loads and fatigue cycles than a comparable cast gear.
Process | Grain Structure | Strength | Applications |
Casting | Random | Medium | Low-stress, non-critical parts |
Machining Only | Cut Grain | Medium | Standard fasteners, fittings |
Forging | Directional | High | High-performance shafts, fasteners, gears |
Reduced Defects and Porosity
Forging significantly reduces internal defects such as porosity and shrinkage cavities. The compressive deformation closes internal voids and increases material density, resulting in superior structural integrity.
This defect reduction is especially important for components used in high-load or safety-critical applications, where internal flaws can lead to premature failure.
Superior Mechanical Properties
Forged steel typically exhibits higher strength-to-weight ratio, better fatigue resistance, and improved toughness. Heat treatment after forging further enhances hardness and performance consistency.
These mechanical advantages make forged steel ideal for components that must withstand repeated loading, vibration, or impact during long-term operation.
Forged Steel vs Cast Steel: Strength and Durability Comparison
When comparing forged steel vs cast steel, forged steel offers higher tensile strength, improved fatigue resistance, and longer service life. These benefits result from refined grain flow and reduced internal defects.
Cast steel provides greater design flexibility for complex shapes but is typically less durable under demanding mechanical conditions. For shafts, gears, rings, flanges, and structural parts, forged steel is generally the preferred choice.
Applications of Forged Steel
At Weforging Manufacturing, we produce custom forgings for industries such as automotive, energy, and heavy equipment. Examples include:
- Ring forgings for wind turbines
- Forged gears for transmission systems
- Heavy-duty fasteners for structural applications
- Shafts, flanges, and custom mechanical assemblies
- Reduce after-sales maintenance costs and enhance brand value
All these parts rely on forged steel’s superior load-bearing capacity and extended service life.
Environmental and Cost Benefits
Although forging can seem more expensive initially, its long-term value is clear:
- Less material waste compared to machining from billet
- Longer product lifespan reduces replacement costs
- Higher efficiency reduces downtime
- Suitable for recycling, aligning with sustainability goals
Conclusion
Forged steel is stronger because controlled deformation refines grain flow and reduces internal defects, resulting in higher strength, better fatigue resistance, and more reliable long-term performance than cast or machined steel.
For industrial components operating under heavy loads or cyclic stress, forged steel offers a more predictable and durable solution. If you are comparing material options for a specific application, reviewing performance requirements early in the design stage can help reduce long-term risk. Drawings or technical details can be shared for an initial discussion if needed.

