What Is Closed Die Forging
Closed die forging, also known as impression die forging, is a widely applied metal forming method where heated billets are shaped inside enclosed dies. This process delivers consistent quality, tight tolerances, and superior mechanical strength. Unlike open die forging, which allows freer material flow, closed die forging ensures precise dimensional control, making it ideal for large-scale production and safety-critical industries. This article outlines the process, advantages, applications, and key factors buyers should evaluate when selecting a forging supplier.
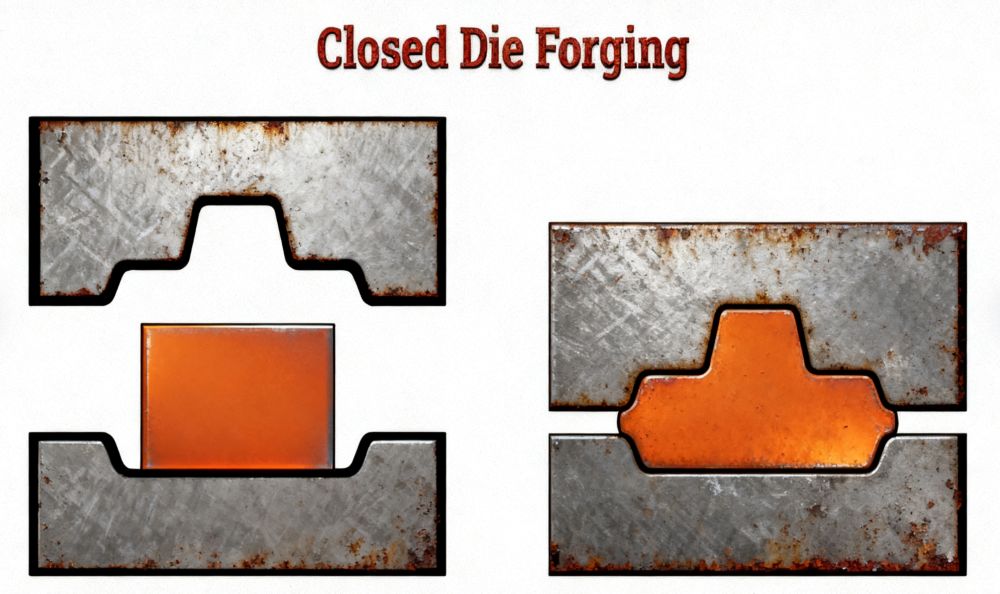
Understanding the Closed Die Forging Process
The closed die forging process begins by heating billets, typically steel or aluminum, to around 1,100–1,250°C. The billet is placed into a precision die cavity that mirrors the final component shape. Under immense pressure, the metal flows to fill the cavity, ensuring accuracy and repeatability. Excess metal, called flash, is expelled and later trimmed.
The quality of the forging die is critical, as it must withstand extreme loads while maintaining dimensional accuracy. Unlike open die forging, which allows freer material flow, closed die forging provides superior consistency and tight tolerances, making it indispensable for industries with strict requirements.
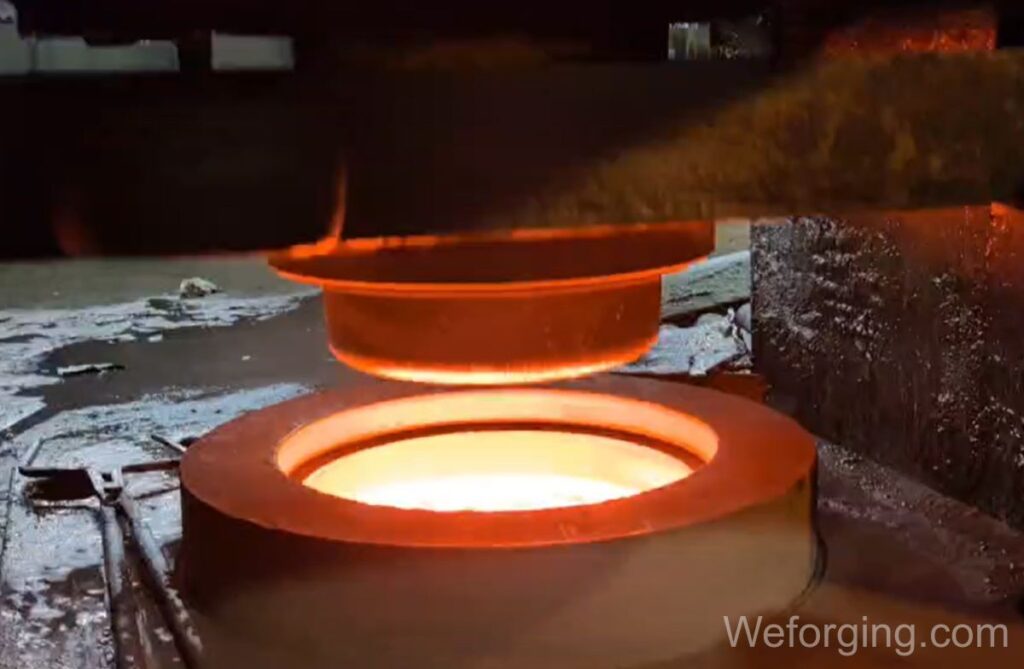

Closed Die Forging Press Types
Closed die forging requires high-capacity presses to generate sufficient force for accurate deformation. The two most common press types are mechanical presses and hydraulic presses.
Mechanical presses provide high-speed cycles and are suitable for small to medium-sized parts requiring high productivity.
Hydraulic presses apply force gradually and are often used for larger or more complex components where controlled deformation is critical.
Press capacities range from several hundred to over 10,000 tons, depending on part size, material, and complexity.
Advantages of Closed Die Forging
High strength – Grain flow refinement improves toughness, fatigue resistance, and load capacity. Ideal for safety-critical applications.
Tight tolerances – Near-net shapes reduce secondary machining, shorten production time, and lower manufacturing cost.
Material flexibility – Supports carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and aluminum for strength or corrosion requirements.
Cleaner production – Generates less waste and fewer finishing steps compared with casting or open die forging.
Better surface finish – Confined dies create smooth surfaces and accurate contours with minimal polishing.
Applications of Closed Die Forging
Closed die forging is widely used in industries where strength, safety, and dimensional accuracy are essential.
Automotive industry
Used for crankshafts, connecting rods, gear blanks, and axle shafts that operate under vibration, torque, and long service cycles.Aerospace manufacturing
Applied to turbine discs, landing gear components, and structural fittings requiring high strength-to-weight ratios and repeatable quality.Industrial machinery and energy sectors
Used for shafts, flanges, and load-bearing components designed for heavy loads, elevated temperatures, and demanding operating conditions.
Across these industries, closed die forging supports reliable performance while maintaining cost efficiency at production scale.
When Should You Use Closed Die Forging?
Closed die forging is used when parts require high strength, tight tolerances, and consistent quality. It is ideal for components exposed to vibration, impact, or heavy cyclic loads.
Typical applications include:
- Automotive safety components
- Aerospace structural fittings
- Industrial shafts and flanges
- Precision mass-production parts
Compared with casting, closed die forging improves grain flow, fatigue resistance, and service life. When reliability and repeatability are critical, it becomes the preferred manufacturing method.

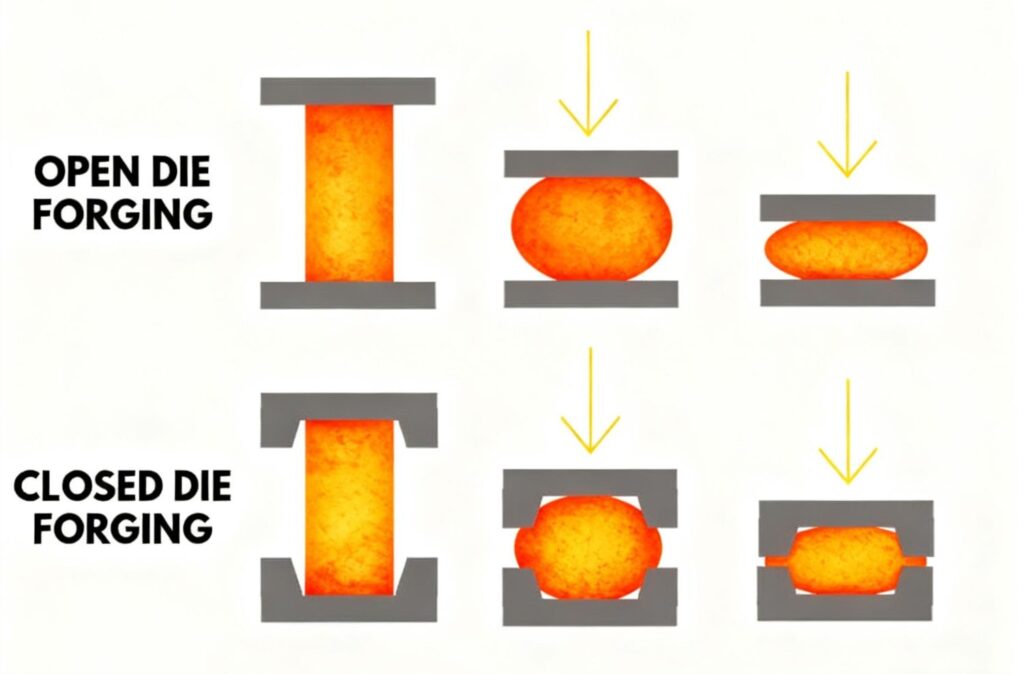
Closed Die Forging vs. Open Die Forging
Closed die forging is used for precision, repeatable mass production.
Open die forging is used for large, simple, or custom components.
Closed Die Forging
- Tight dimensional tolerances
- High repeatability in batch production
- Suitable for small to medium parts
- Higher production efficiency
- Ideal for precision OEM components
Open Die Forging
- Flexible shaping for large parts
- Suitable for simple or oversized geometry
- Lower tooling constraints
- Better for custom or low-volume production
- Used in heavy industrial forgings
Closed Die Forging vs. Casting: Key Differences
| Comparison Factor | Closed Die Forging | Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Grain structure | Continuous grain flow improves strength and fatigue resistance | Solidification structure may contain internal porosity or discontinuities |
| Mechanical strength | High strength and impact resistance | Lower structural consistency under heavy load |
| Fatigue performance | Excellent for cyclic and vibration loading | Reduced fatigue resistance in stress-critical parts |
| Dimensional tolerance | Tight tolerances and repeatable accuracy | Greater dimensional variation |
| Surface finish | Smooth near-net shape surface | Often requires additional machining or finishing |
| Structural reliability | Predictable performance for safety-critical parts | Performance depends heavily on casting quality |
| Design flexibility | Best for precision load-bearing components | Suitable for complex shapes and hollow features |
| Service life | Longer lifecycle under heavy stress | Shorter lifecycle in high-load environments |
Why Is Closed Die Forging Stronger Than Casting?
Closed die forging is stronger than casting because pressure forces the metal to flow and align its grain structure instead of cooling randomly. This creates higher density and better load distribution.
Key reasons include:
- Continuous grain flow that follows part geometry
- Reduced porosity compared with cast structures
- Higher fatigue and impact resistance
- More consistent mechanical properties
- Improved reliability under cyclic loads
Forged parts deliver predictable strength for critical industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Forging Supplier
When selecting a reliable supplier, buyers should focus on:
- Quality Assurance – Testing methods such as ultrasonic, hardness checks, and metallography.
- Forging Die Expertise – Well-engineered dies ensure accurate and consistent production.
- Production Capacity – Ability to handle diverse order sizes, from small precision parts to heavy-duty components.
- CNC Machining Integration – Ensures tight tolerances and final surface finishes.
- Delivery Reliability – On-time supply reduces costly downtime.
A supplier with integrated forging, machining, and inspection processes can reduce coordination risk and improve overall project efficiency.
At Weforging, closed die forging is combined with CNC machining and structured quality control to support OEM projects across automotive, energy, and heavy industrial applications
Conclusion
Closed die forging combines strength, dimensional accuracy, and repeatability, making it one of the most trusted manufacturing methods. Its advantages in mass production and safety-critical applications have ensured its position as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
At Weforging, we bring together forging expertise, CNC finishing, and strict quality assurance to provide high-performance solutions for industries worldwide.
Contact us today to learn more about our closed die forging services and how we can support your next project.
F.A.Q.
Closed die forging offers superior strength, tighter tolerances, and longer fatigue life than cast components. It also reduces defects like porosity and ensures consistent quality across mass production.
Key sectors include hydraulic cylinder components, gearbox parts, ring gear transmissions, heavy vehicle components, damping systems, and critical mechanical or equipment parts in nuclear power. These fields require highly precise and durable components such as cylinder ends, drive shafts, gears, turbine discs, ring gears, and shafts.
They should evaluate the supplier’s quality control system, the integration of forging and CNC machining capabilities, inspection processes, alignment with customer application requirements, die design expertise, CNC precision level, production capacity, and delivery reliability. Choosing an experienced supplier like Weforging ensures compliance with international standards such as ISO and AGMA, guaranteeing consistent quality and performance

