Custom Open Die Forging: Design Flexibility and Manufacturing Considerations
Custom open die forging is widely applied to large and non-standard forged components that benefit from flexible geometry, material selection, and manufacturing routes. The process supports adaptable production planning, making it well suited for low- to medium-volume industrial projects. From a procurement perspective, the focus is on identifying when custom open die forging aligns with specific project needs. This article outlines how design flexibility, manufacturing considerations, and material standards shape custom open die forging decisions, helping engineering and procurement teams define requirements with clarity before production begins.

What Is Custom Open Die Forging?
Open die forging is a forging process in which metal is shaped between flat or simple dies without fully enclosing the workpiece. In custom applications, this process allows forged components to be produced in a wide range of sizes and geometries. Custom open die forging is commonly used for shafts, rings, blocks, and other large components where dimensional flexibility and material integrity are important considerations.
When Should Procurement Consider Custom Open Die Forging?
This section offers a concise decision checklist frequently used by procurement teams. From a sourcing and planning perspective, custom open die forging is often evaluated in the following scenarios:
— Components with large dimensions or application-specific geometries
— Projects involving focused or project-based production volumes
— Programs where design parameters or specifications are being finalized
— Applications requiring flexible material grade selection or multi-standard compliance
— Sourcing plans that benefit from coordinated forging and machining workflows
Why Design Flexibility Matters in Open Die Forging
Design flexibility is one of the main reasons open die forging is widely applied to large and non-standard industrial components. The process allows designers to define cross-sections, lengths, and structural transitions with a high degree of freedom, making it well suited for components produced in limited quantities.
Open die forging also accommodates a wide range of material options, enabling material grades to be selected based on performance requirements such as strength, toughness, and service conditions. Together, this flexibility in both geometry and material selection supports designs that closely match application-specific requirements.
Key Design Considerations for Custom Open Die Forging
Forging Shape and Section Transitions
When designing custom open die forgings, smooth section transitions are commonly preferred to support stable deformation during forging. Gradual changes in cross-section help maintain material flow continuity and provide a favorable starting point for subsequent machining operations.
Tolerances and Machining Allowance
Open die forgings are typically produced with machining allowance to accommodate final dimensional requirements. Defining appropriate tolerances at the design stage helps ensure that forged components can be efficiently machined to the required accuracy while maintaining dimensional consistency.
Manufacturing Considerations in Custom Open Die Forging
Forging Process Flow Overview
The open die forging process generally includes controlled heating, incremental deformation, and dimensional adjustment. Each step is coordinated to achieve the desired shape while maintaining material integrity. Process planning focuses on repeatability and dimensional stability rather than high-volume output.
Coordination Between Forging and Machining
Custom open die forgings are often produced as semi-finished components that are later CNC machined. Early coordination between forging design and machining strategy helps define reference surfaces, machining allowance, and inspection points, supporting a smoother production flow.
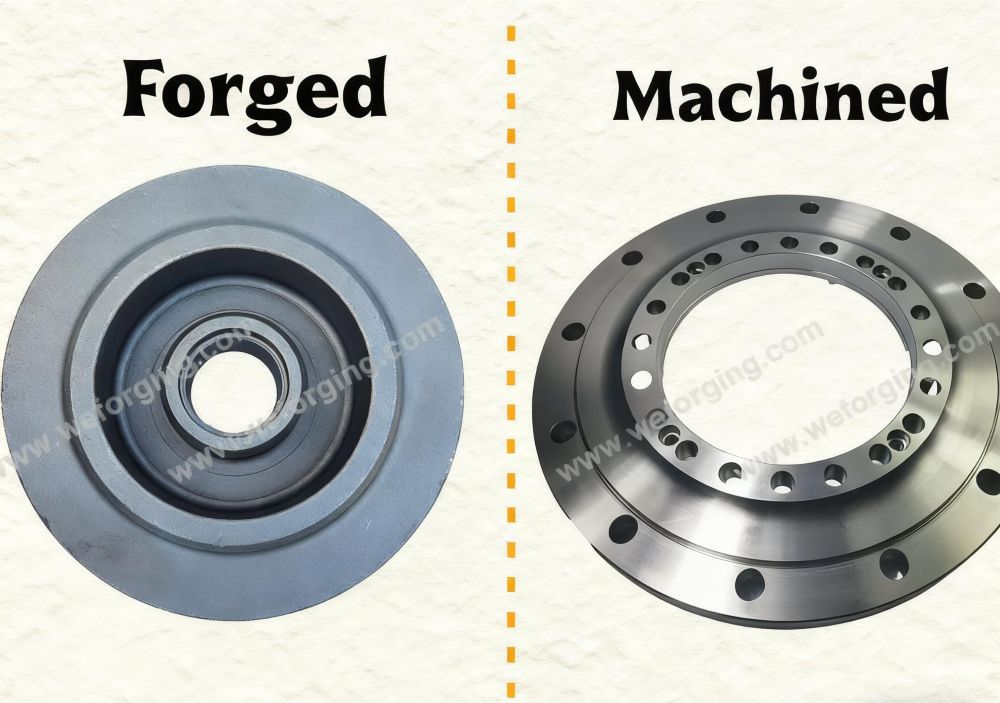
Materials and Standards for Custom Open Die Forgings
Common Materials Used in Open Die Forging
Materials for custom open die forgings are selected based on mechanical performance, component size, and service conditions. Carbon steels, alloy steels, and stainless steels are commonly used to support a wide range of industrial applications.
Applicable International Standards
Open die forged components are commonly produced according to international standards such as ASTM, EN/DIN, and ISO. Typical material grades include ASTM A105, A182, A694, as well as EN/DIN grades like 42CrMo4 and 34CrNiMo6. For global projects, material equivalency is often evaluated to support consistent mechanical performance across regions.
Open Die Forging vs Closed Die Forging
Open die forging and closed die forging serve different manufacturing needs. The open die forging is commonly used for large, custom, or low-volume components where flexibility in geometry and material selection is important. Closed die forging is typically applied to smaller parts produced in higher volumes with defined shapes. The choice between these processes depends on component size, quantity, design requirements, and overall production planning.
Typical Applications
Custom open die forging is widely applied across industrial sectors that require adaptable component designs and material solutions. Its flexibility supports a broad range of applications, including:
— Heavy machinery components, such as large shafts and structural blocks, designed to support specific load requirements and installation configurations.
— Energy and power equipment, where forged rings and shafts are selected to match material performance with operating conditions.
— Industrial transmission and structural systems, utilizing large forged rings and blocks that support dimensional adaptability and reliable material performance.

Conclusion
Custom open die forging provides a flexible manufacturing approach for large and non-standard components. By defining geometry, material selection, applicable standards, and manufacturing coordination early in the design stage, engineering and procurement teams can support efficient production planning and consistent results.
For project-specific questions, our engineering team provides free technical consultation and responds within 24 hours.


