What Is Gear Hobbing?
Modern gear manufacturing relies on precise and repeatable machining processes to achieve accurate tooth geometry and stable performance. Among common gear cutting methods, gear hobbing is widely used for producing external gears with consistent quality and high efficiency. The process combines continuous cutting motion with controlled synchronization between the cutting tool and the workpiece, making it suitable for both industrial production and precision gear applications.
This article provides a practical overview of gear hobbing, explaining how the process works, the role of machines and cutting tools, and where it is commonly applied, helping engineers, buyers, and project managers better understand gear manufacturing and sourcing decisions.

What Is Gear Hobbing?
Gear hobbing is a gear cutting method in which a rotating cutting tool, known as a hob, gradually generates gear teeth on a cylindrical workpiece. Compared with form cutting, the tooth profile is produced through the relative motion between the tool and the blank instead of relying on a single fixed shape.
This generating principle allows the process to produce accurate tooth geometry while maintaining flexibility for different gear sizes and modules. As a result, gear hobbing is commonly used for manufacturing spur gears, helical gears, and worm gears in a wide range of industrial applications.
Because the cutting action is continuous, the process supports stable cutting conditions and consistent results across multiple parts, making it a practical choice for both small and large production runs.
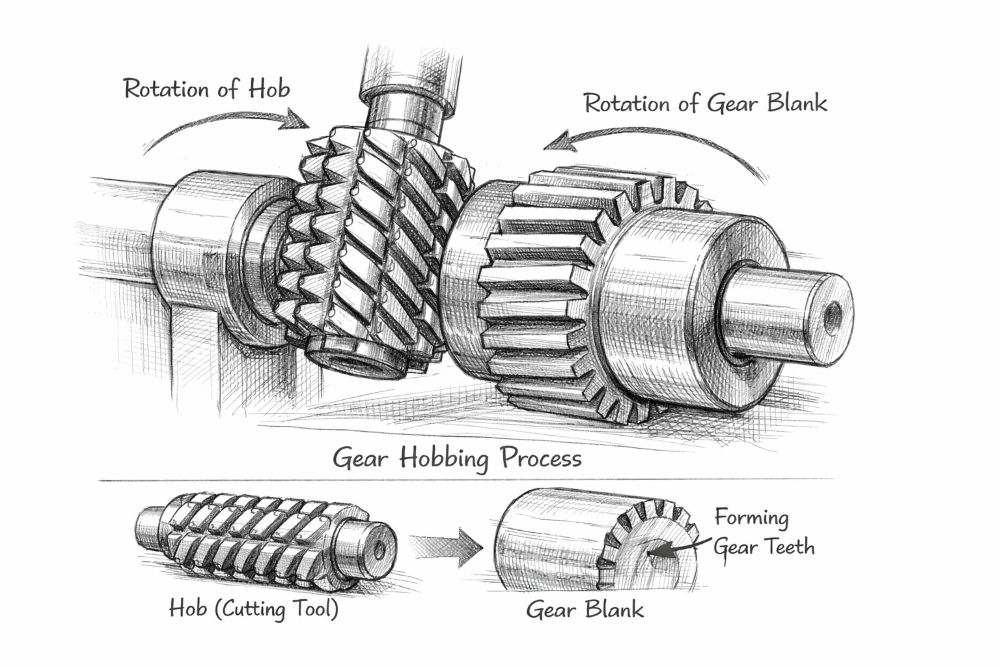
How the Gear Hobbing Process Works
The gear hobbing process is based on synchronized rotation between the hob cutter and the gear blank. As the hob rotates, it progressively removes material while the workpiece turns at a controlled speed. This coordinated movement ensures that each tooth is generated accurately along the gear circumference.
During machining, the hob advances axially across the workpiece, gradually forming the full tooth width. Cutting parameters such as feed rate, cutting speed, and depth are selected based on gear material, module, and surface finish requirements.
Because the cutting motion is continuous rather than intermittent, the process supports smooth material removal and uniform tooth formation. This contributes to consistent gear geometry and predictable dimensional results in finished components.
Gear Hobbing Machines and Their Role in Accuracy
Gear hobbing machines are built to ensure accurate coordination between the cutting tool and the workpiece. Modern equipment commonly uses CNC control systems to manage spindle rotation, feed movement, and indexing functions in a stable and controlled manner.
A typical machine setup includes:
A hob spindle for tool rotation
A workpiece spindle for gear blank positioning
Axial and radial feed mechanisms
CNC control for coordinated motion
Machine performance plays an important role in maintaining consistent tooth geometry and surface quality. CNC-based systems also allow flexible parameter adjustment, supporting consistent results across a wide range of gear designs.

Typical Applications
Gear hobbing is widely applied in industries that require reliable power transmission and precise motion control. Common application areas include:
- Automotive systems – transmission gears, differential gears
- Industrial machinery – reduction gears and drive systems
- Construction equipment – motion and rotation components
- Energy equipment – mechanical transmission elements
The process is especially suitable for external gears produced in medium to high volumes, where consistency and efficiency are important considerations.
Gear Hobbing for Custom Gear Manufacturing
Gear hobbing is widely used in custom gear manufacturing because it accommodates diverse gear designs, materials, and production requirements. By adjusting cutting parameters and tool setups, the process supports various modules, tooth counts, face widths, and helix angles, making it suitable for both standard and project-specific gear specifications.
In custom applications, gear hobbing is often combined with forged gear blanks to support stable material structure and efficient machining. Forging provides a reliable starting form, while gear hobbing enables accurate tooth generation before CNC finishing, heat treatment, and inspection. This integrated approach helps align gear geometry, mechanical properties, and application requirements.
When to Use Gear Hobbing Services
Many manufacturers choose to work with specialized gear hobbing services rather than maintaining in-house gear cutting capacity. Outsourced services are commonly selected when projects involve multiple gear variants, short lead times, or integration with forging and machining operations.
Gear hobbing services are often used in combination with:
- Forged gear blanks
- CNC machining for finishing operations
- Heat treatment and inspection processes
At companies such as Weforging, gear hobbing is offered as part of an integrated manufacturing route that combines forging, precision machining, and quality control within a single production system. This coordinated approach helps streamline production flow, maintain dimensional consistency, and align machining quality with final application requirements.
Conclusion
Gear hobbing is widely used in modern gear manufacturing for its efficiency and ability to produce accurate, repeatable tooth profiles. With proper machine control and tool selection, the process supports consistent gear quality across a range of industrial applications.
For projects involving forged gear blanks or precision gear machining, feel free to contact our team to discuss your technical requirements.

