What Is a Pinion Gear?
A pinion gear is one of the most essential components in modern mechanical transmission systems. In a typical gear and pinion arrangement, the pinion is the smaller gear that drives or is driven by a larger mating gear to transmit motion, torque, and speed. From industrial machinery to automotive assemblies, pinion gears play a critical role in ensuring precise and efficient power transfer. This article explains what a pinion gear is, how it works, the common types used in industry, and why it is widely adopted across engineering applications.

What Is a Pinion Gear and How Does It Work?
A pinion gear is typically the smaller of two meshing gears, functioning as either the driving or driven element of the gear system. Its main purpose is to transmit power efficiently while controlling torque and speed according to the gear ratio. Because it contains fewer teeth than its mating gear, the pinion usually rotates faster and experiences higher contact stress. This makes the material selection and heat treatment of pinion gears critical to long-term reliability.
In a standard gear and pinion mechanism, the pinion engages with a larger gear wheel or ring gear. The relationship between their tooth counts determines the speed reduction or multiplication. Smooth operation relies on the accuracy of the tooth profile—most commonly involute profiles—which ensures minimal friction, controlled backlash, and stable torque delivery. High-quality pinion gears also incorporate optimized surface hardness and core toughness to withstand repeated loading cycles.
Common Types of Pinion Gears
Spur Pinion Gear
A spur pinion gear features straight and parallel teeth. It is simple, efficient, and cost-effective, making it ideal for general-purpose machinery, elevators, packaging equipment, and light-duty reducers. This design represents the traditional spur and pinion gear setup.
Helical Pinion Gear
Helical pinions feature angled teeth that allow multiple teeth to engage at once, providing smoother and quieter operation. They are commonly used in automotive transmissions, industrial gearboxes, and heavy-duty machinery.
Bevel and Spiral Bevel Pinion
These pinions allow torque transmission at right angles and are essential components in differential systems and angular gear drives. Spiral bevel pinions offer improved tooth strength and smoother contact.
Internal Pinion
Used in planetary gear sets and compact hydraulic drives, internal pinions mesh with gears containing inward-facing teeth.
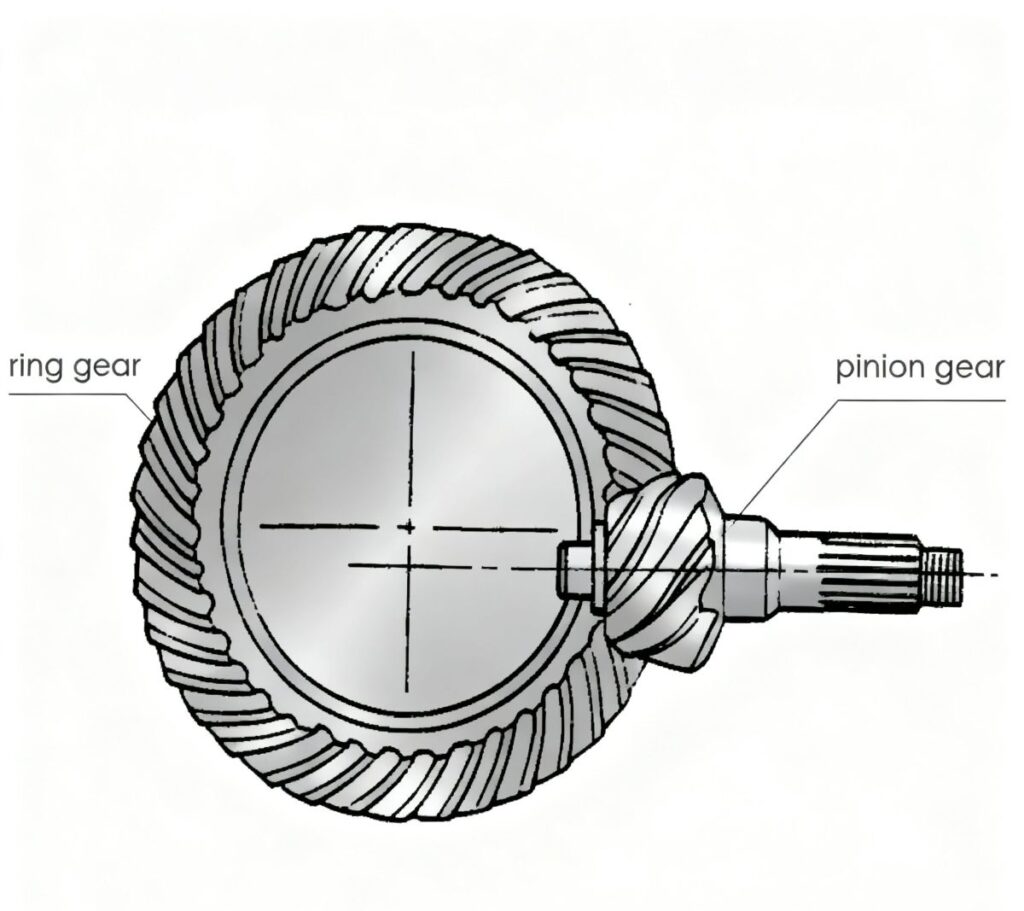
Ring and Pinion Gears in Heavy-Duty Machinery
In many high-load applications, pinion gears operate together with larger gears as ring and pinion gears. This arrangement is widely used in automotive differentials, off-road machinery, mining equipment, and construction vehicles.
The pinion transfers input torque into the ring gear, creating the necessary torque multiplication. A precisely manufactured pinion ring gear ensures stable tooth contact, reduced vibration, and consistent performance, even under continuous or shock-loading conditions.
These gear sets are typically produced from forged alloy steels such as 42CrMo or 8620 materials. After forging, they undergo CNC machining, gear hobbing or shaping, carburizing, quenching, grinding, and quality inspection. Proper tooth hardness (HRC 58–62) and optimized tooth profiles greatly improve wear resistance and fatigue strength.
Rack and Pinion Gear for Linear Motion
A rack and pinion gear mechanism converts rotational movement into linear motion, making it essential in CNC equipment, robotic systems, steering units, and lifting machines. In the steering assembly shown, the input shaft drives the pinion inside the pinion housing, which then moves the rack left or right. Components such as the valve body housing, hydraulic lines, cylinder, boots, and inner tie rods support smooth, assisted steering and protect the system from contaminants.
Applications include:
– CNC axis drives
– Robotic arms
– Steering systems
– Industrial lifting platforms
– Automated storage equipment
Precision machining, lubrication, and backlash control are crucial to long-term stability.

Materials and Manufacturing of Pinion Gears
The performance of a pinion gear depends largely on the material selection and manufacturing process. High-quality pinions are typically produced from alloy steels such as 42CrMo, 20CrMnTi, SCM440, or equivalent grades selected for strength, toughness, and heat-treatment compatibility.
Typical Production Workflow
- Forging or machining of blanks for improved grain structure
- Rough turning to establish initial dimensions
- Gear hobbing or shaping to cut teeth
- Carburizing or quenching and tempering to increase surface hardness
- Grinding or honing for precision tooth geometry
- Final inspection including hardness testing, gear measuring, and NDT
This integrated process ensures that each pinion gear achieves the correct balance of strength, wear resistance, and dimensional accuracy.
Advantages of High-Quality Pinion Gears
Using well-designed and precisely manufactured pinion gears provides several benefits:
- High load capacity due to dense forged structures
- Improved durability through advanced heat treatment
- Consistent meshing accuracy for smooth power transmission
- Reduced noise and vibration thanks to precise tooth contact patterns
- Lower maintenance costs and extended service intervals
- Better reliability in gear and pinion systems under continuous or high-speed operation
These advantages make forged pinion gears ideal for industries where performance and reliability are essential.
When to Choose a Custom Pinion Gear Solution
Standard pinion gears may not always meet specialized requirements. Custom designs become necessary when:
- Equipment requires a specific module, tooth count, or pressure angle
- Space constraints demand a unique gear ratio or shaft configuration
- The application involves high torque, shock loads, or continuous operation
- Integration into a ring and pinion or linear motion system requires tailored specifications
Manufacturers like Weforging provide complete solutions combining forging, CNC machining, gear hobbing, grinding, heat treatment, and inspection under one system. This ensures tighter tolerances, improved performance consistency, and shorter lead times for OEM machinery builders and engineering teams.
Conclusion
Pinion gears are essential for reliable torque transmission, precise motion control, and stable long-term performance. Their design, materials, and manufacturing quality directly affect system efficiency in gear drives, rack-and-pinion mechanisms, and heavy-duty equipment. For applications requiring high strength, accuracy, or custom specifications, high-quality pinion gears provide a dependable engineering solution.
If you need custom pinion gears, ring-and-pinion sets, or complete transmission solutions, contact our engineering team. We can support your drawings, working conditions, and provide fast, professional quotations.

